In Bash scripting, the if statement allows you to make decisions based on conditions. It executes commands based on whether a specified condition is true or false.
if [ condition ]; then
# commands
fi
The basic syntax involves using if followed by the condition in square brackets and the commands to execute.
Let's look at some examples of how to use if statements in Bash:
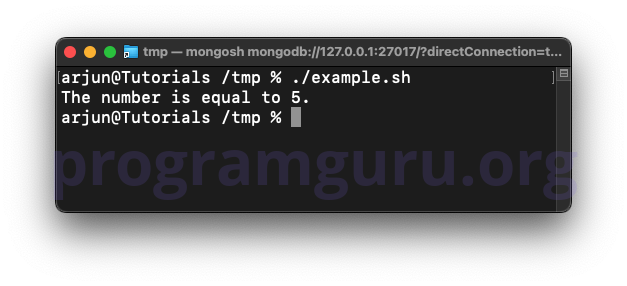
This script checks if the variable number is equal to 5 and prints a message if it is.
#!/bin/bash
number=5
if [ $number -eq 5 ]; then
echo "The number is equal to 5."
fi
In this script, the variable number is assigned the value 5. The if statement checks if number is equal to 5 using the -eq operator, and if true, prints a message.
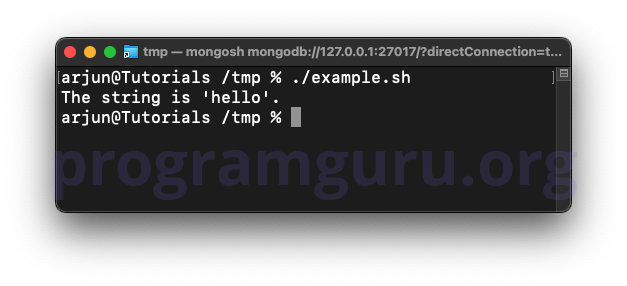
This script checks if the variable string is equal to 'hello' and prints a message if it is.
#!/bin/bash
string="hello"
if [ "$string" = "hello" ]; then
echo "The string is 'hello'."
fi
In this script, the variable string is assigned the value 'hello'. The if statement checks if string is equal to 'hello' using the = operator, and if true, prints a message.
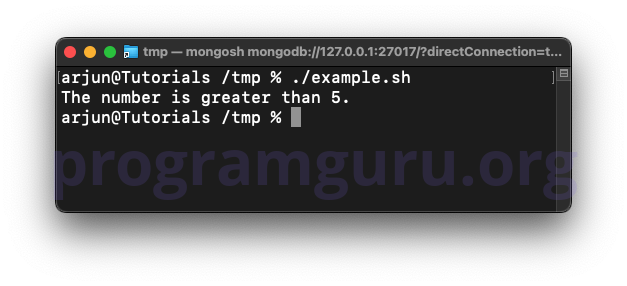
This script checks if the variable number is greater than 5 and prints a message if it is.
#!/bin/bash
number=10
if [ $number -gt 5 ]; then
echo "The number is greater than 5."
fi
In this script, the variable number is assigned the value 10. The if statement checks if number is greater than 5 using the -gt operator, and if true, prints a message.
The Bash if statement is a crucial tool for conditional operations in shell scripting. Understanding how to use simple if statements can help you create more dynamic and responsive scripts.