The MySQL WHERE clause is used to filter records. It is essential for querying specific rows in a table based on conditions.
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
The WHERE clause has the following components:
column1, column2, ...: The columns to be retrieved.table_name: The name of the table from which to retrieve the data.condition: The condition to filter the records.Let's look at some examples of the MySQL WHERE clause:
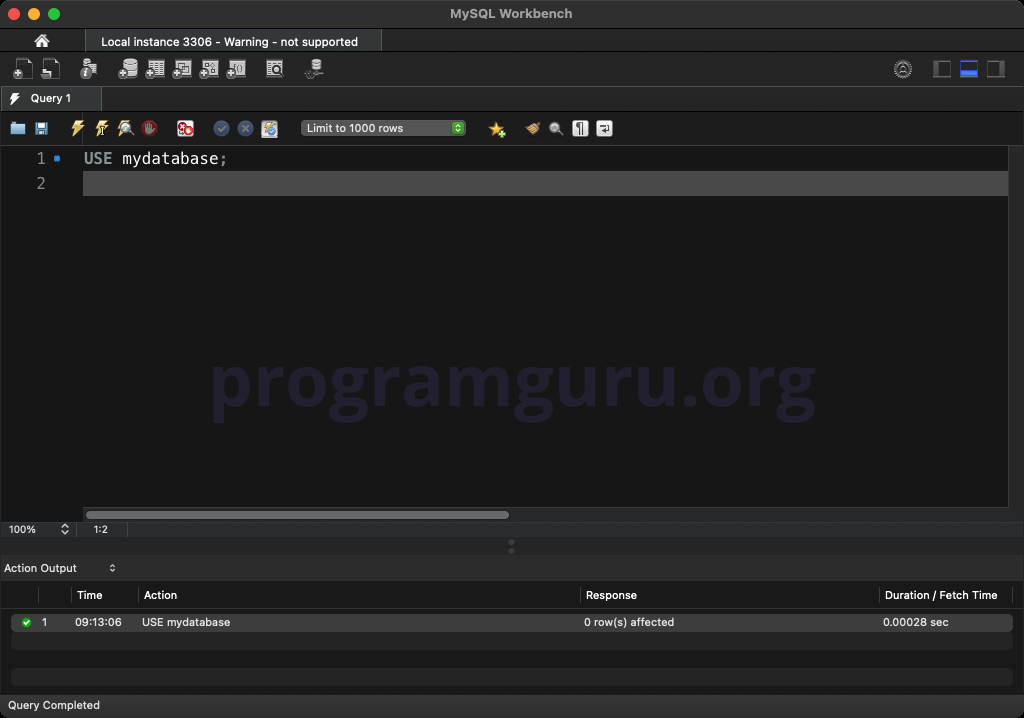
USE mydatabase;
This query sets the context to the database named mydatabase.
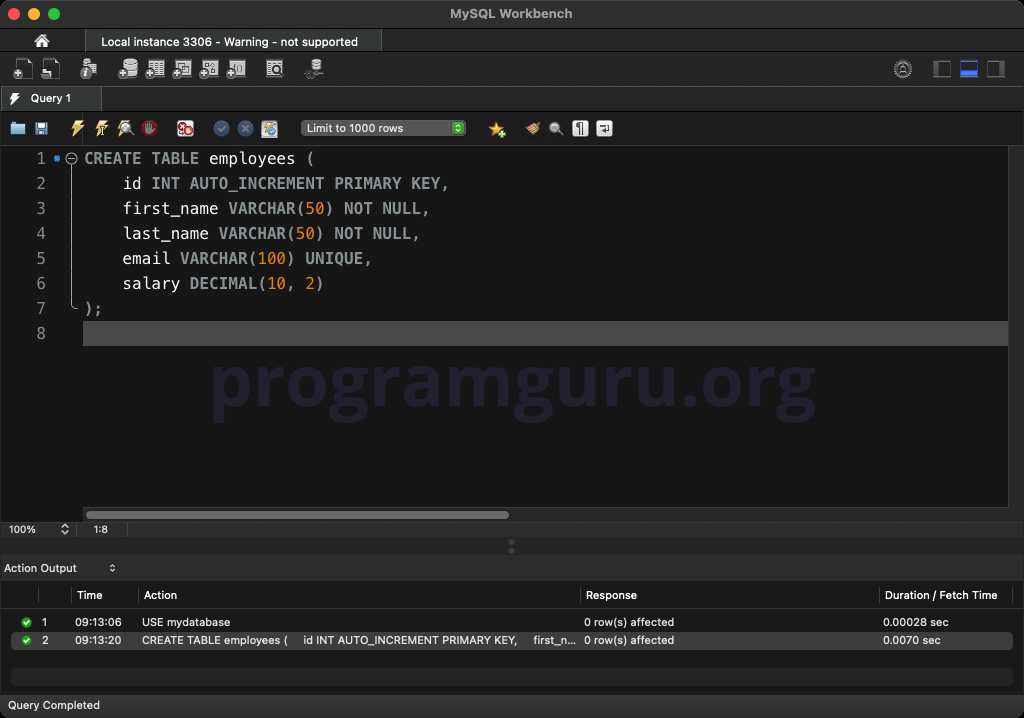
Create a table to work with:
CREATE TABLE employees (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(100) UNIQUE,
salary DECIMAL(10, 2)
);
This query creates a table named employees with columns for id, first_name, last_name, email, and salary.
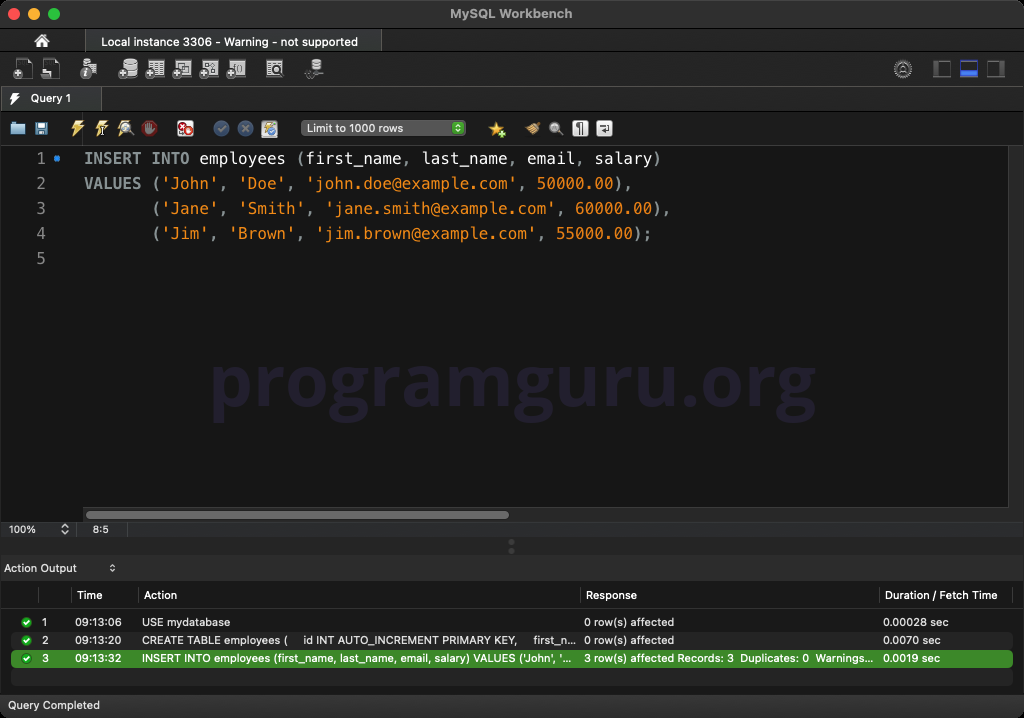
Insert some initial rows into the table:
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, email, salary)
VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 'john.doe@example.com', 50000.00),
('Jane', 'Smith', 'jane.smith@example.com', 60000.00),
('Jim', 'Brown', 'jim.brown@example.com', 55000.00);
This query inserts three rows into the employees table.
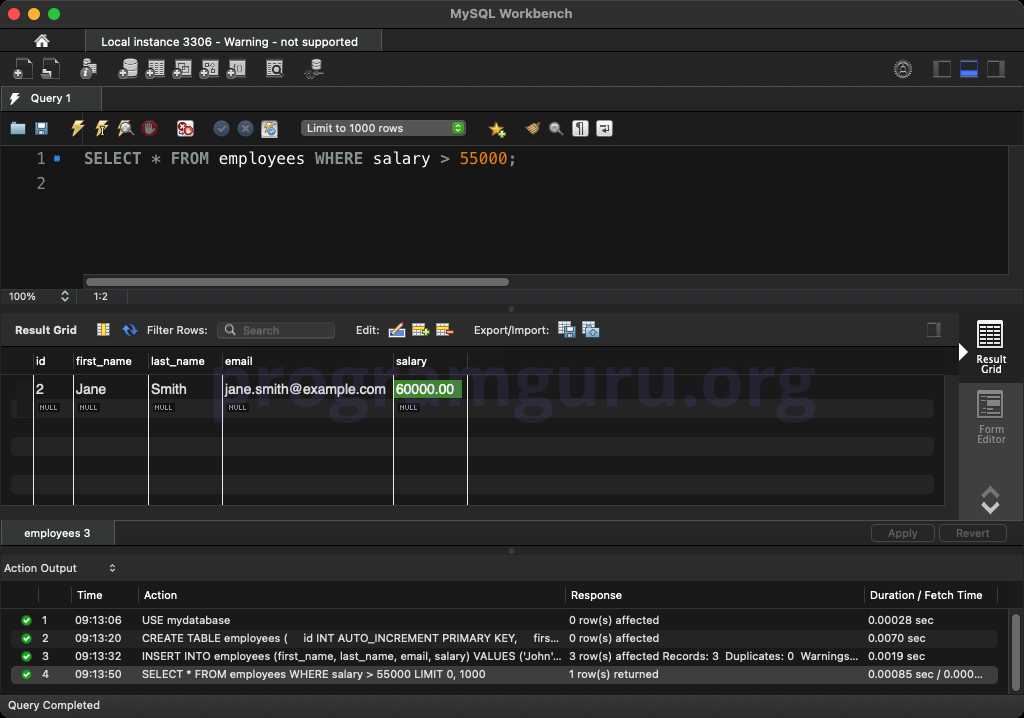
Select rows based on a condition:
SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE salary > 55000;
This query retrieves all columns from rows in the employees table where the salary is greater than 55000.
Select rows based on multiple conditions:
SELECT *
FROM employees
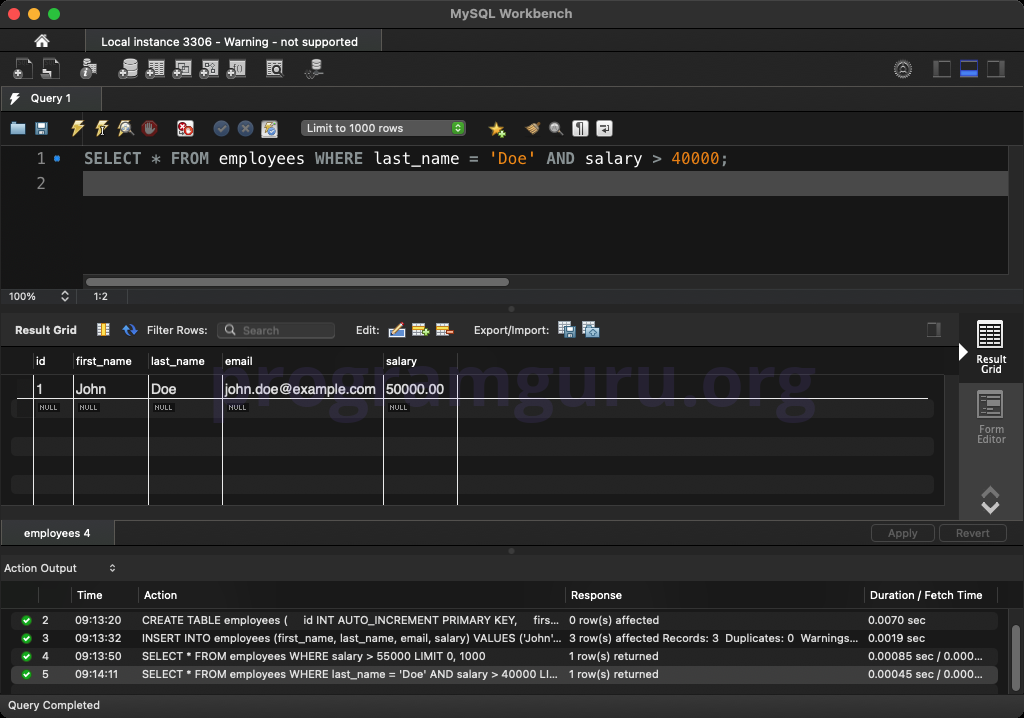
WHERE last_name = 'Doe' AND salary > 40000;
This query retrieves all columns from rows in the employees table where the last_name is 'Doe' and the salary is greater than 40000.
Select rows using the OR operator:
SELECT *
FROM employees
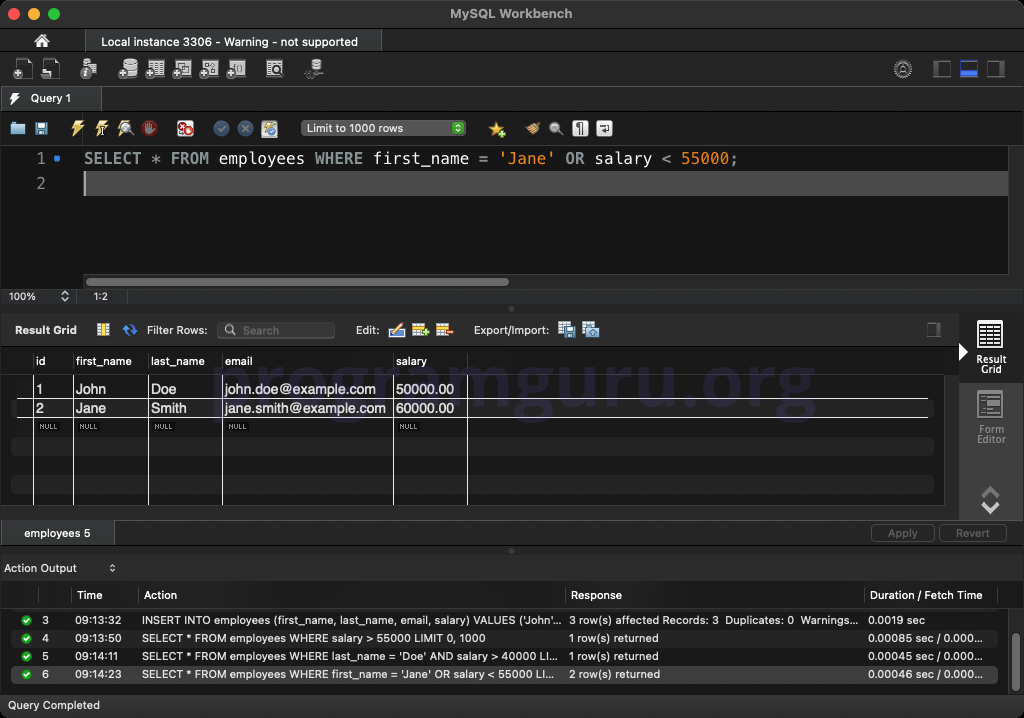
WHERE first_name = 'Jane' OR salary < 55000;
This query retrieves all columns from rows in the employees table where the first_name is 'Jane' or the salary is less than 55000.
Select rows using the BETWEEN operator:
SELECT *
FROM employees
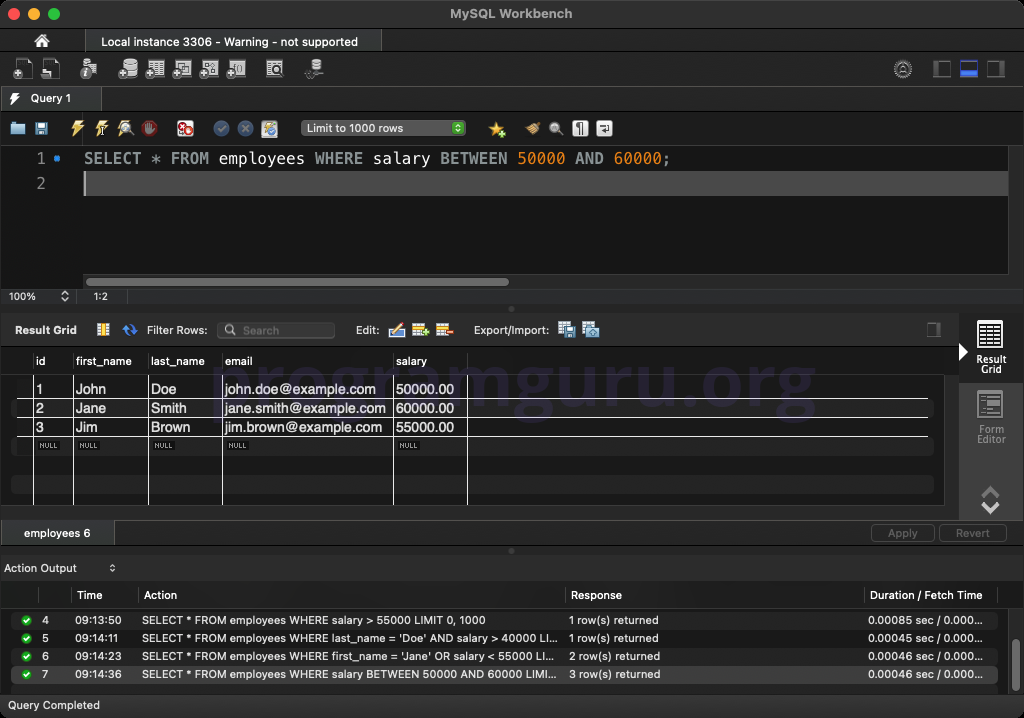
WHERE salary BETWEEN 50000 AND 60000;
This query retrieves all columns from rows in the employees table where the salary is between 50000 and 60000.
Select rows using the IN operator:
SELECT *
FROM employees
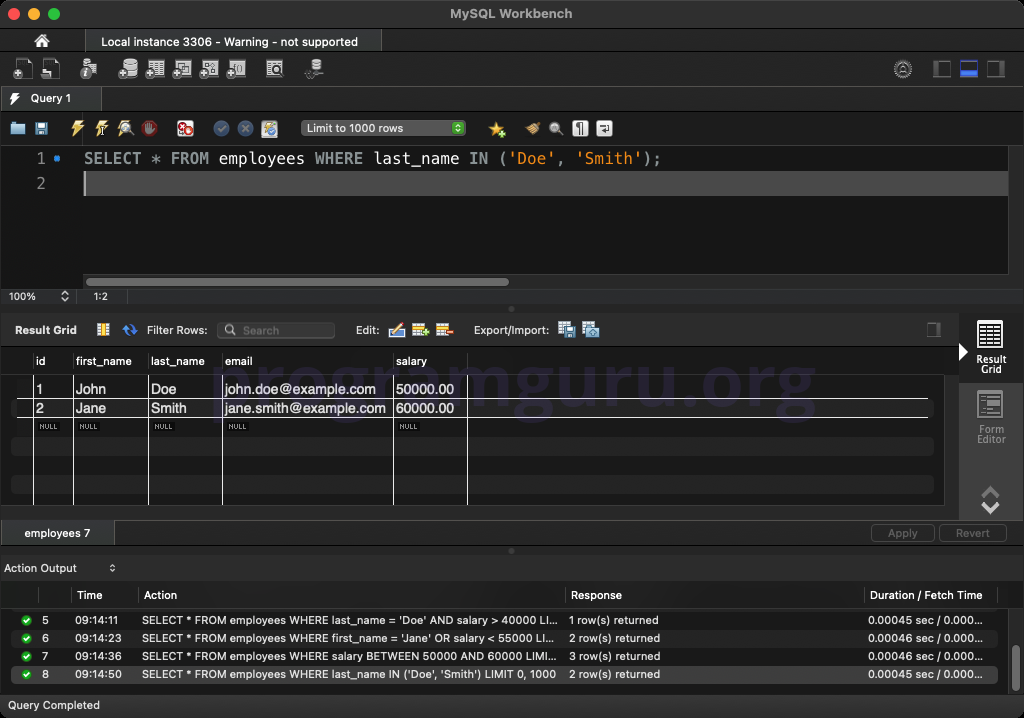
WHERE last_name IN ('Doe', 'Smith');
This query retrieves all columns from rows in the employees table where the last_name is either 'Doe' or 'Smith'.
The MySQL WHERE clause is a powerful tool for filtering records based on specific conditions. Understanding how to use the WHERE clause is essential for effective data querying and analysis in MySQL.